Publications
2025
-
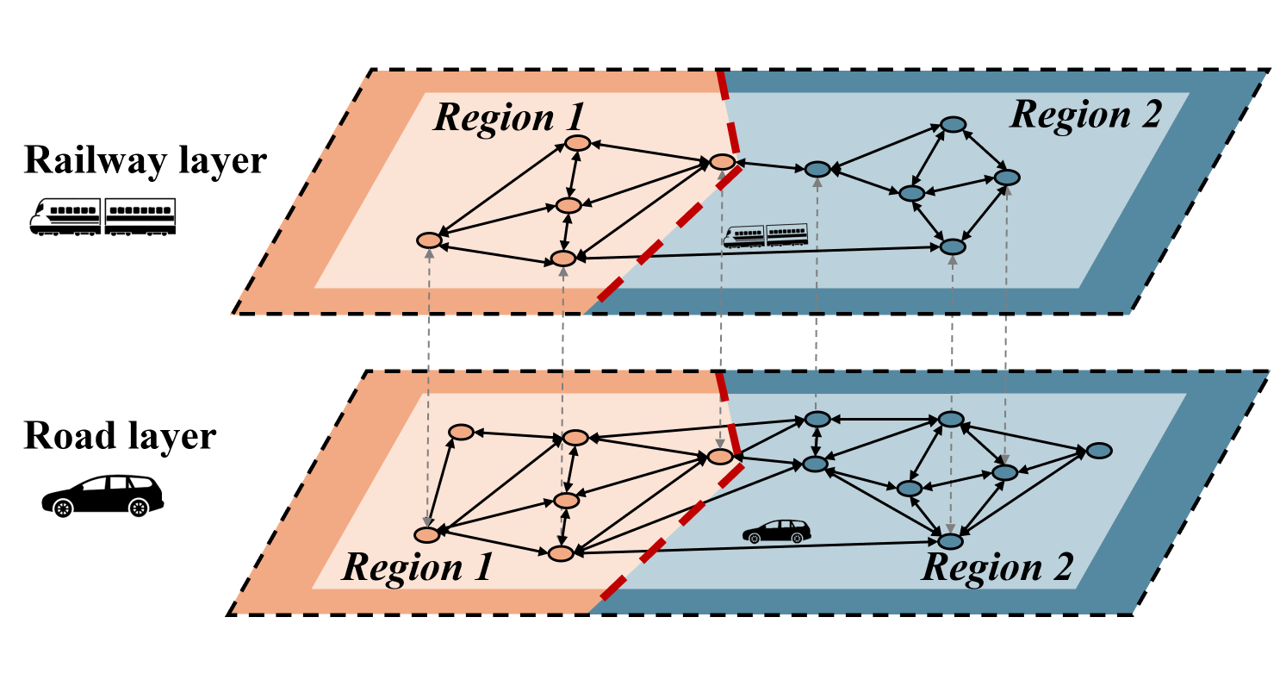 Co-investment with Payoff Sharing Benefit Operators and Users in Network DesignHe M., Censi A., Frazzoli E., and Zardini G.In Proceedings of the 2025 American Control Conference (ACC), 2025
Co-investment with Payoff Sharing Benefit Operators and Users in Network DesignHe M., Censi A., Frazzoli E., and Zardini G.In Proceedings of the 2025 American Control Conference (ACC), 2025Network-based complex systems are inherently interconnected, with the design and performance of subnetworks being interdependent. However, the decisions of self-interested operators may lead to suboptimal outcomes for users. In this paper, we consider the question of what cooperative mechanisms can benefit both operators and users simultaneously. We address this question in a game theoretical setting, integrating both non-cooperative and cooperative game theory. During the non-cooperative stage, subnetwork decision-makers strategically design their local networks. In the cooperative stage, the co-investment mechanism and the payoff-sharing mechanism are developed to enlarge collective benefits and fairly distribute them. A case study of the Sioux Falls network is conducted to demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed framework. The impact of this interactive network design on environmental sustainability, social welfare, and economic efficiency is evaluated, along with an examination of scenarios involving regions with heterogeneous characteristics.
@inproceedings{He2025, author = {M., He and A., Censi and E., Frazzoli and G., Zardini}, title = {Co-investment with Payoff Sharing Benefit Operators and Users in Network Design}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2025 American Control Conference (ACC)}, year = {2025}, } -
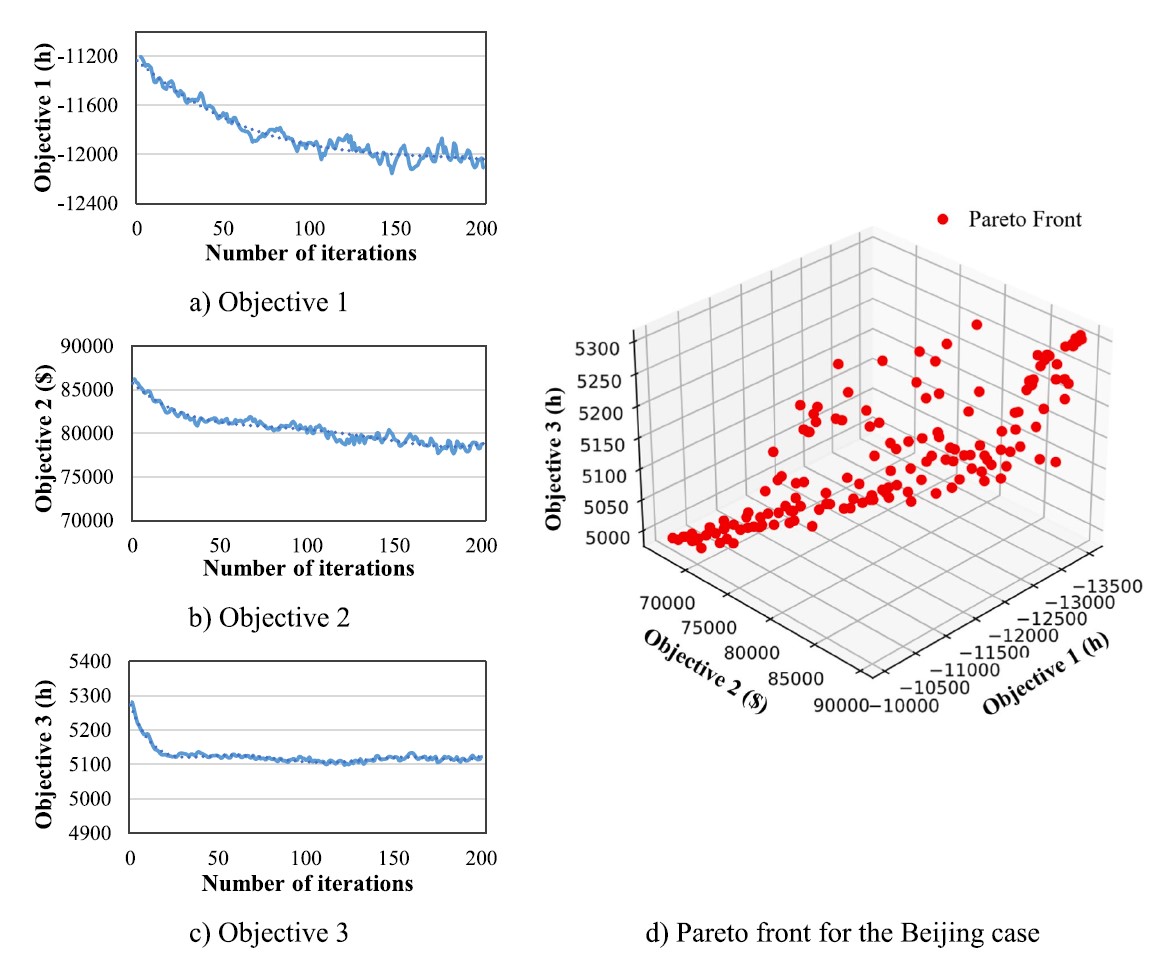
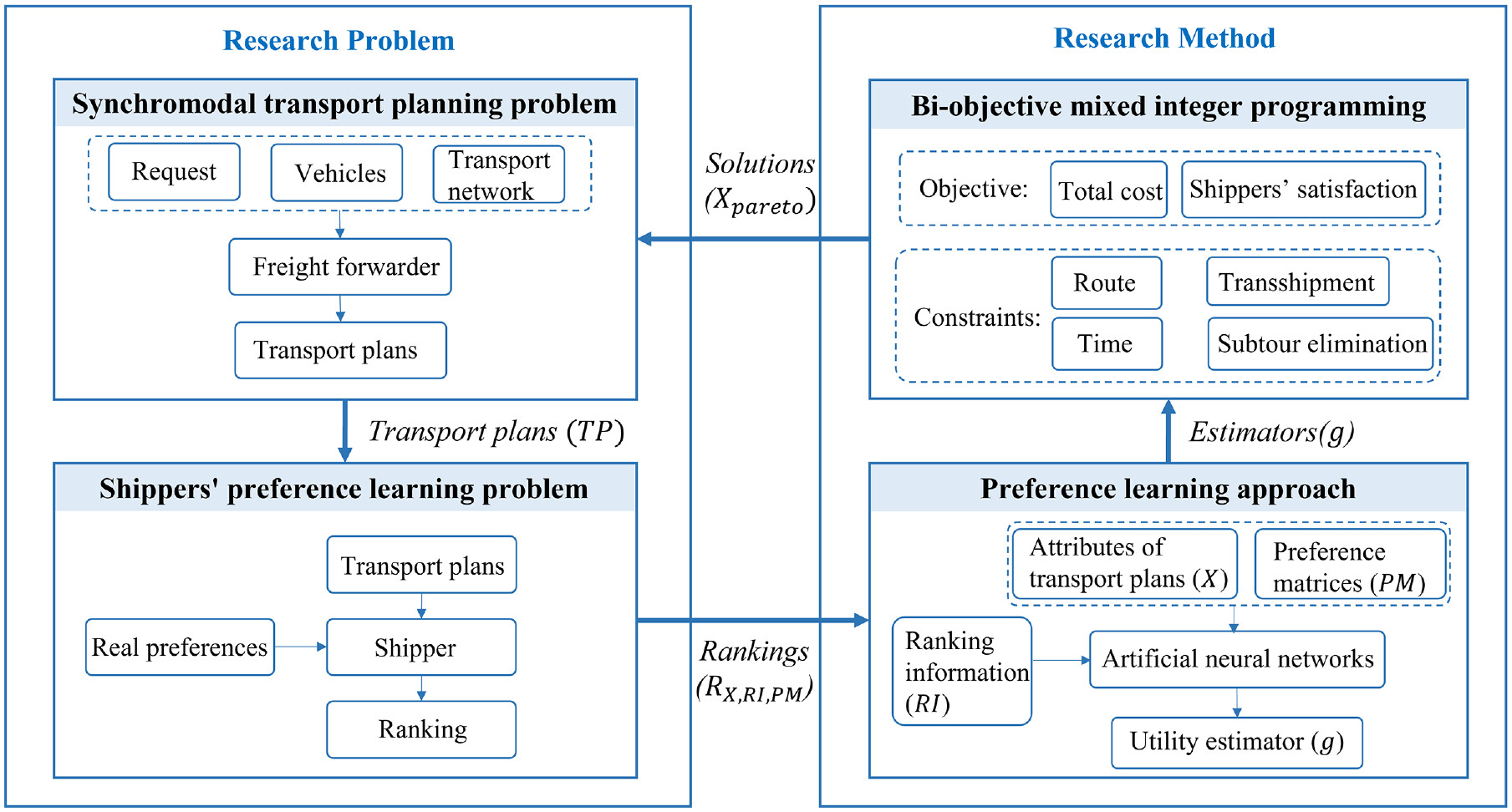 Integrated Synchromodal Transport Planning and Preference LearningHe M.and Zhang Y., and Atasoy B.Transportation Research Record, 2025
Integrated Synchromodal Transport Planning and Preference LearningHe M.and Zhang Y., and Atasoy B.Transportation Research Record, 2025A comprehensive understanding of shippers‘ preferences can help transport freight forwarders create targeted transport services and enhance long-term business relationships. This research proposes an integrated approach to learn shippers‘ preferences in synchromodal transport operations and optimize transport services accordingly. A preference learning method was developed to capture shippers‘ preferences through pairwise comparisons of transport plans. To model the underlying complex nonlinear relationships and detect heterogeneity in preferences, artificial neural networks (NNs) were employed to approximate shippers‘ utility for a specific plan. Leveraging the learned preferences, a synchromodal transport planning model with shippers‘ preferences (STPM-SP) was proposed, with the objectives of minimizing the total transportation cost and maximizing shippers‘ satisfaction. A case study based on the European Rhine-Alpine corridor was conducted to demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed approach. The results demonstrated that artificial NNs have the capacity to identify complex (i.e., nonlinear and heterogeneous) relationships in shippers‘ preferences. The planning results showed that the STPM-SP effectively found solutions with a significant satisfaction improvement of 37%. This research contributes to learning shippers‘ preferences in the transport operation process and highlights the importance of incorporating these preferences into the decision-making process of synchromodal transport planning.
@article{He2025STPM, author = {Y., He M.and Zhang and B., Atasoy}, doi = {10.1177/03611981241310399}, journal = {Transportation Research Record}, title = {Integrated Synchromodal Transport Planning and Preference Learning}, volume = {0}, year = {2025}, }
2023
-
 A data-driven large-scale micro-simulation approach to deploying and operating wireless charging lanesHe M., Wang S., and Zhuge C.Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2023
A data-driven large-scale micro-simulation approach to deploying and operating wireless charging lanesHe M., Wang S., and Zhuge C.Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2023Dynamic wireless charging technology has the potential to promote the uptake of electric freight vehicles (EFVs) by allowing charging on the move. This paper presented a joint DWC lane deployment and operation model based on the trajectory data of actual EFVs. The model was formulated as a multi-objective mixed-integer programming model, with objectives to maximize saved charging time, minimize charging cost, and minimize negative impact on traffic. The model considered various constraints related to investment, facility construction, and charging decisions of EFV drivers. It was first tested on a small network and was further applied into a large-scale scenario in Beijing. The results suggested that DWC could reduce charging time by approximately 0.08–0.11 h per EFV per day within an investment limit of 67 million dollars. The deployment of DWC can be long-term profitable, resulting in a net value of 140.83 million dollars over a 25-year period.
@article{He2023, author = {M., He and S., Wang and C., Zhuge}, doi = {10.1016/j.trd.2023.103835}, issn = {13619209}, journal = {Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment}, title = {A data-driven large-scale micro-simulation approach to deploying and operating wireless charging lanes}, volume = {121}, year = {2023}, } -
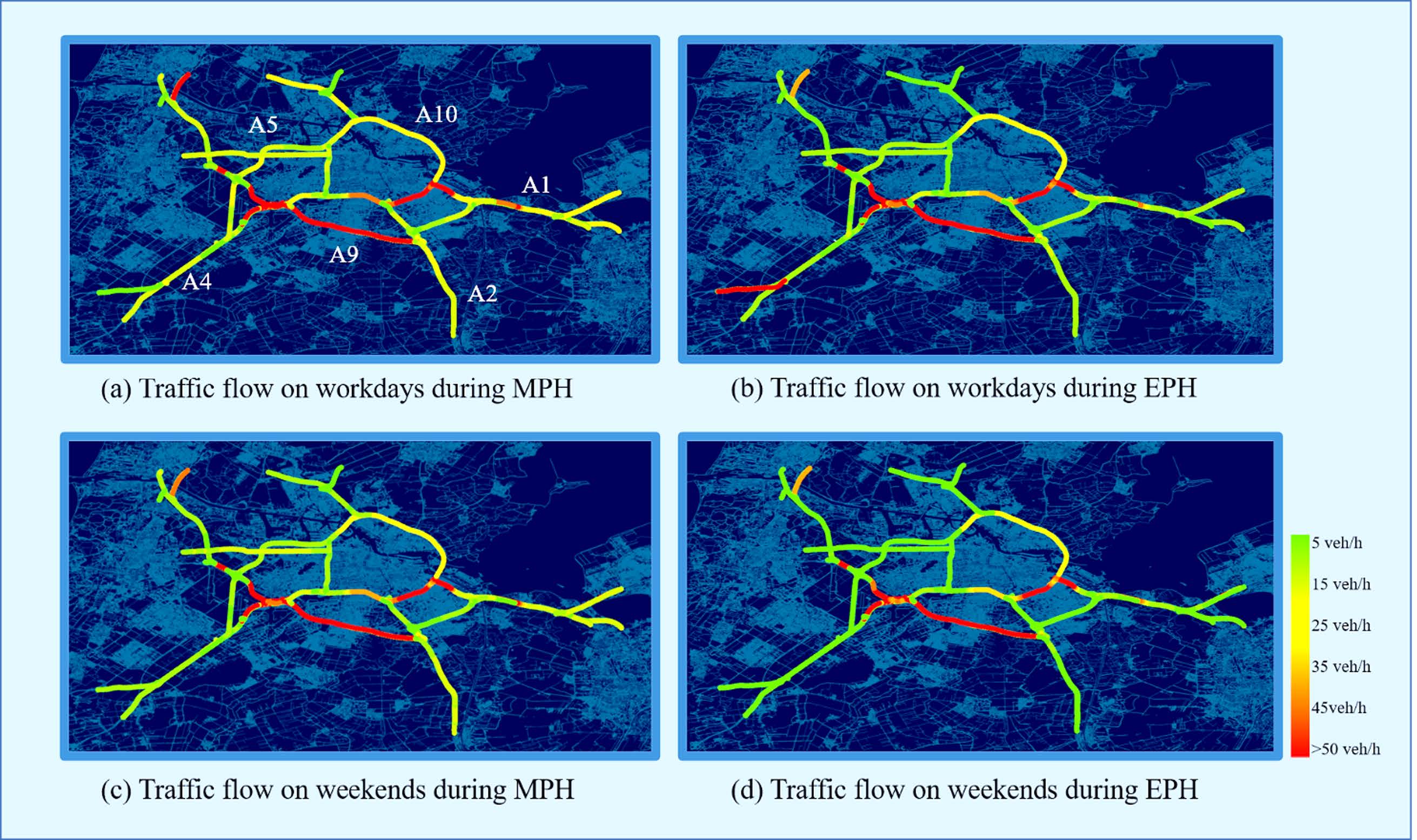 A data-driven integrated framework for fast-charging facility planning using multi-period bi-objective optimizationHe M., Krishnakumari P., Luo D., and Chen J.2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2023
A data-driven integrated framework for fast-charging facility planning using multi-period bi-objective optimizationHe M., Krishnakumari P., Luo D., and Chen J.2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2023With the electrification in freight transportation, the availability of fast-charging facilities becomes essential to facilitate en-route charging for freight electric vehicles. Most studies focus on planning charging facilities based on mathematical modeling and hypothetical scenarios. This study aims to develop a data-driven integrated framework for fast-charging facility planning. By leveraging the highway traffic data, we extracted, analyzed, and compared spatial and temporal flow patterns of general traffic and freight traffic. Furthermore, graph theory-based network evaluation methods are employed to identify traffic nodes within the highway network that play a significant role in accommodating charging infrastructure. A candidate selection method is proposed to obtain potential deployment locations for charging stations and to-go chargers. Based on this, we present a multi-period bi-objective optimization model to provide optimal solutions for the placement of charging facilities, with the objectives of minimizing investment cost and maximizing demand coverage. The case study on the Amsterdam highway network shows how existing traffic data can be used to generate more realistic charging demand scenarios and how it can be integrated and evaluated within the optimization framework for facility planning. The study also shows that the proposed model can leverage the potential of early investment in improving the charging demand coverage.
@article{He2023itsc, author = {M., He and P., Krishnakumari and D., Luo and J., Chen}, journal = {2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC)}, title = {A data-driven integrated framework for fast-charging facility planning using multi-period bi-objective optimization}, year = {2023}, }
2022
-
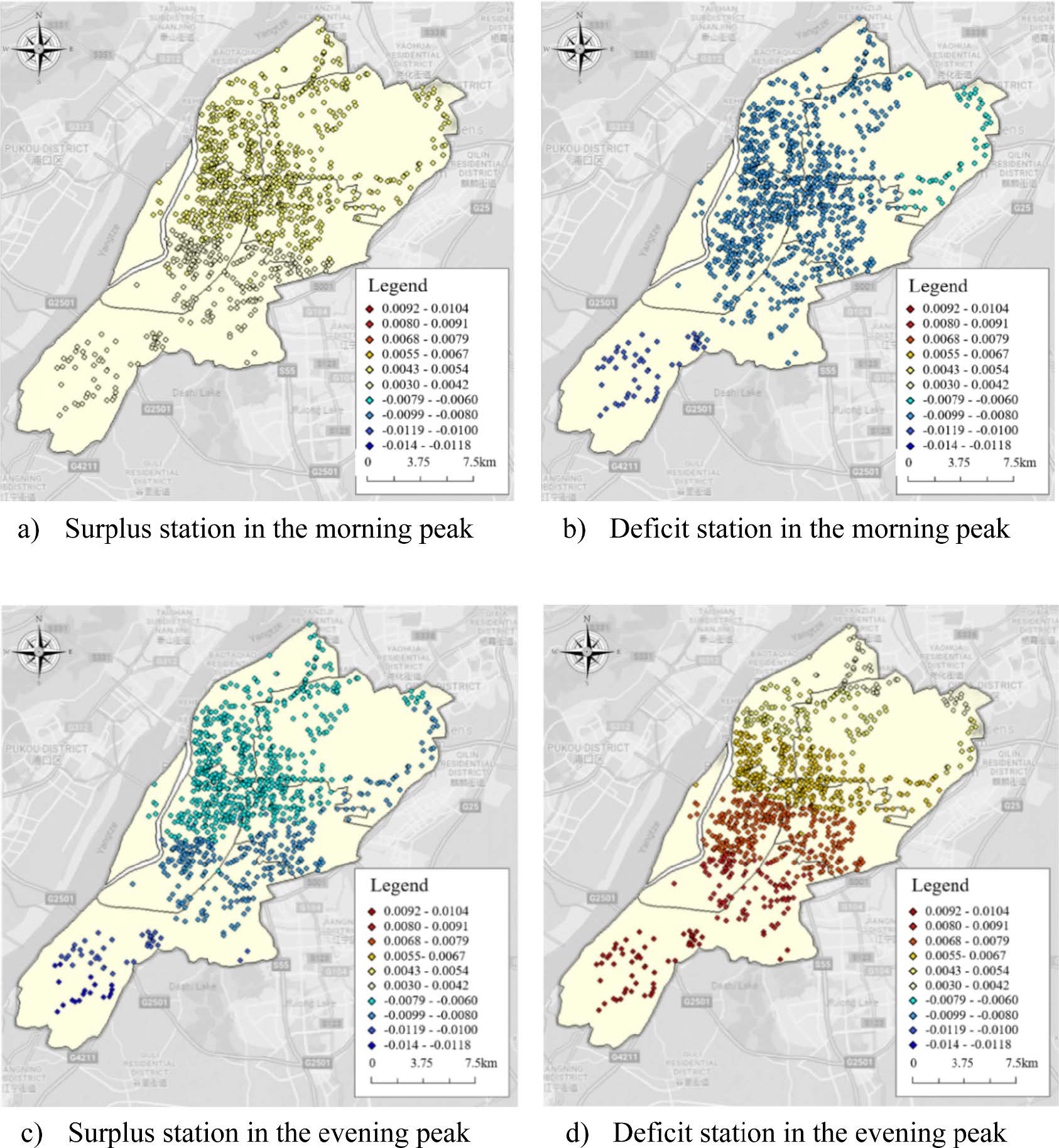 Geographically Weighted Multinomial Logit Models for Modelling the Spatial Heterogeneity in the Bike-Sharing Renting-Returning Imbalance: A Case Study on Nanjing, ChinaHe M., Ma X., Wang J., and Zhu M.Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022
Geographically Weighted Multinomial Logit Models for Modelling the Spatial Heterogeneity in the Bike-Sharing Renting-Returning Imbalance: A Case Study on Nanjing, ChinaHe M., Ma X., Wang J., and Zhu M.Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022Bike-sharing systems have promoted transportation sustainability in cities. Shared bikes can be used for short-distance trips or accessing public transport systems. However, the asymmetric spatiotemporal distribution of bikes across stations has become a major barrier that hinders bike-sharing adoption in cities. Before implementing policies to tackle this issue effectively, it is necessary to understand the unevenly distributed shared bikes across stations. This study proposed methods to identify the renting-returning imbalance at the station level using Nanjing bike-sharing trip dataset. Next, this study compared the spatiotemporal characteristics of imbalanced bike-sharing usage during different periods (morning peak, evening peak, and non-peak). Finally, geographically weighted multinomial logit models (GWMNL) were established to reveal the influence of exogenous variables on the renting-returning imbalance. Model results suggested that work-related points of interest (POI) could positively impact the renting-returning imbalance during peak periods. Higher population density could result in the bike-sharing renting-returning imbalance in the morning peak, and it contributed to the balance of bike-sharing in the evening. In the morning peak, higher land use mix and older people could ease the imbalance of bike-sharing. In the evening peak, longer travel time has negative impacts in most places in the study area. Based on these findings, this study provided implications for transportation planners and policymakers to balance bike-sharing systems and improve the overall service quality.
@article{He2022, author = {M., He and X., Ma and J., Wang and M., Zhu}, doi = {10.1016/j.scs.2022.103967}, issn = {22106707}, journal = {Sustainable Cities and Society}, title = {Geographically Weighted Multinomial Logit Models for Modelling the Spatial Heterogeneity in the Bike-Sharing Renting-Returning Imbalance: A Case Study on Nanjing, China}, volume = {83}, year = {2022}, }
2021
-
 Station importance evaluation in dynamic bike-sharing rebalancing optimization using an entropy-based TOPSIS approachHe M., Ma X., and Jin Y.IEEE Access, 2021
Station importance evaluation in dynamic bike-sharing rebalancing optimization using an entropy-based TOPSIS approachHe M., Ma X., and Jin Y.IEEE Access, 2021As an eco-friendly travel mode, bike-sharing has prevailed around the world. However, the systems are imbalanced due to the asymmetric spatial and temporal distribution of user demand. Station prioritization strategies are needed to rebalance more shared bikes for more important stations. This paper proposes an evaluation method of station importance in dynamic bike-sharing rebalancing. Firstly, a shortterm demand prediction model is applied to capture the temporal and spatial characteristics of bike-sharing trip data and predict bike-sharing demand at the station level. Based on the prediction results, the method of determining rebalancing quantity is proposed with consideration of bike-sharing usage throughout the rebalancing period. Then, three criteria are employed to evaluate the importance of bike-sharing stations, including rebalancing quantity, closeness to inventory threshold, and distance from the key station. An entropy-based Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) approach is proposed to weigh different criteria and evaluate station importance. Furthermore, the experiments on bike-sharing data from Nanjing City demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods. This research is helpful for operators and managers to dynamically rebalance shared bikes with high efficiency and improve the service quality of bike-sharing systems.
@article{He2021, author = {M., He and X., Ma and Y., Jin}, doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3063881}, issn = {21693536}, journal = {IEEE Access}, title = {Station importance evaluation in dynamic bike-sharing rebalancing optimization using an entropy-based TOPSIS approach}, volume = {9}, year = {2021}, }
2018
-
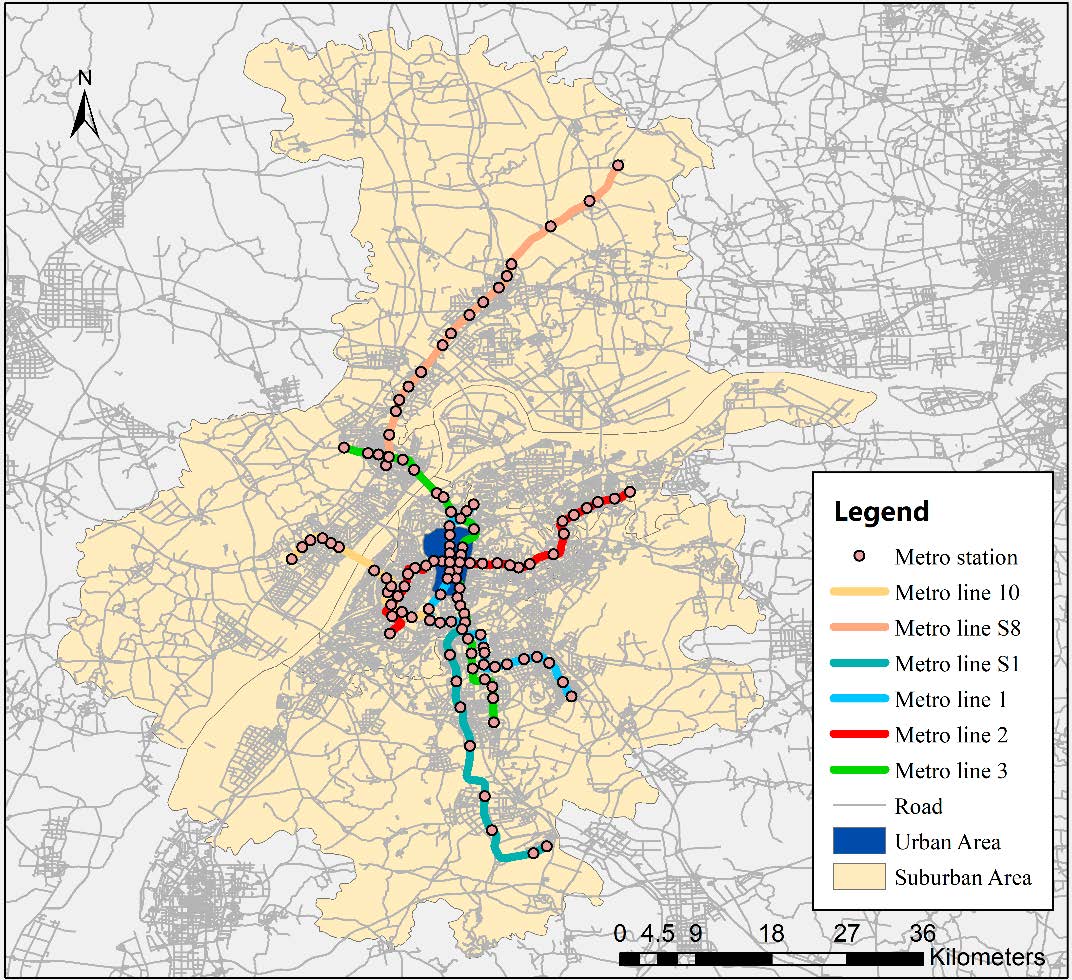 Measuring bikeshare access/egress transferring distance and catchment area around metro stations from smartcard dataMa X., Jin Y., and He M.Information, 2018
Measuring bikeshare access/egress transferring distance and catchment area around metro stations from smartcard dataMa X., Jin Y., and He M.Information, 2018Metro-bikeshare integration is considered a green and efficient travel model. To better develop such integration, it is necessary to monitor and analyze metro-bikeshare transfer characteristics. This paper measures access and egress transferring distances and catchment areas based on smartcard data. A cubic regression model is conducted for the exploration of the 85th access and egress network-based transferring distance around metro stations. Then, the independent samples t-test and one-way analysis of variance are used to explore access and egress transfer characteristics in demographic groups and spatial and temporal dimension. Additionally, the catchment area is delineated by applying both the network-based distance method and Euclidean distance method. The result reveals that males outcompete females both in access and egress distances and urban dwellers ride a shorter distance than those in suburban areas. Access and egress distances are both shorter in morning peak hours than those in evening peak hours and access distance on weekdays is longer than that on weekends. In addition, network-based catchment area accounts for over 90% of Euclidean catchment area in urban areas, while most of the ratios are less than 85% in suburban. The paper uses data from Nanjing, China as a case study. This study serves as a scientific basis for policy makers and bikeshare companies to improve metro-bikeshare integration.
@article{Ma2018, author = {X., Ma and Y., Jin and M., He}, doi = {10.3390/info9110289}, issn = {20782489}, issue = {11}, journal = {Information}, title = {Measuring bikeshare access/egress transferring distance and catchment area around metro stations from smartcard data}, volume = {9}, year = {2018}, } -
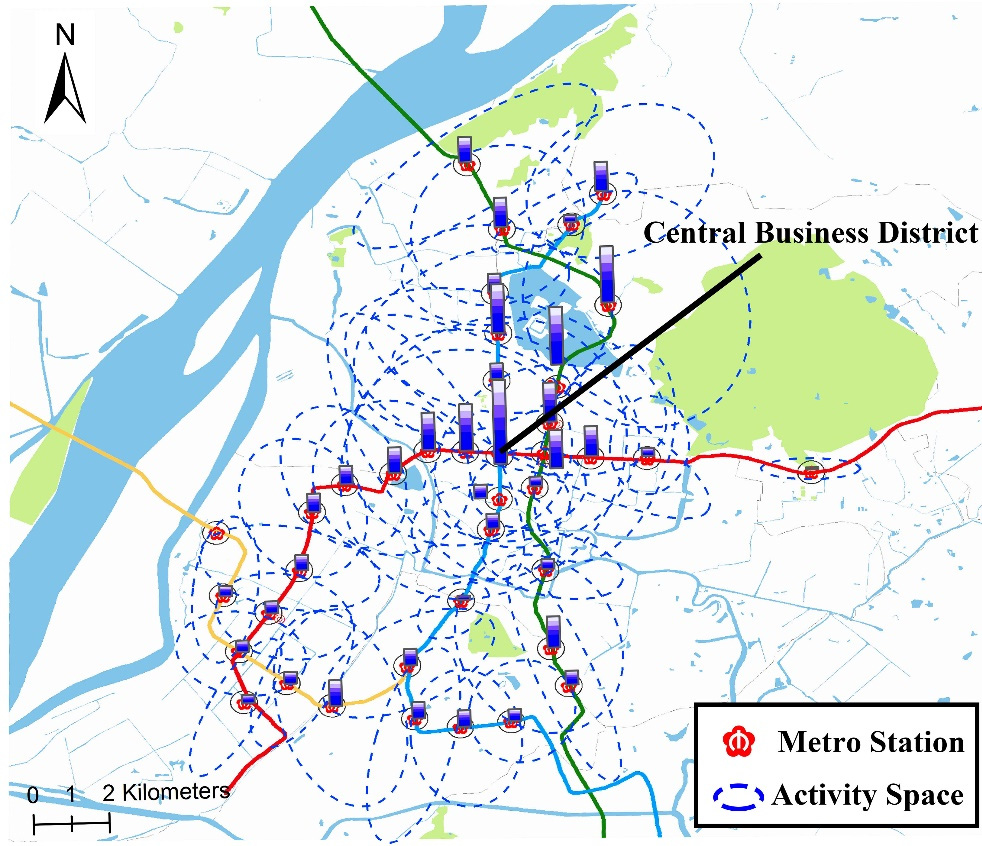 Modeling the factors influencing the activity spaces of bikeshare around metro stations: A spatial regression modelMa X., Ji Y., Jin Y., Wang J., and He M.Sustainability, 2018
Modeling the factors influencing the activity spaces of bikeshare around metro stations: A spatial regression modelMa X., Ji Y., Jin Y., Wang J., and He M.Sustainability, 2018Metro-bikeshare integration is considered a green and efficient travel model. To better understand bikeshare as a feeder mode to the metro, this study explored the factors that influence the activity spaces of bikeshare around metro stations. First, metro-bikeshare transfer trips were recognized by matching bikeshare smartcard data and metro smartcard data. Then, standard deviation ellipse (SDE) was used for the calculation of the metro-bikeshare activity spaces. Moreover, an ordinary least squares (OLS) regression and a spatial error model (SEM) were established to reveal the effects of social-demographic, travel-related, and built environment factors on the activity spaces of bikeshare around metro stations, and the SEM outperformed OLS significantly in terms of model fit. Results show that the average metro-bikeshare activity space on weekdays is larger than that on weekends. The proportion of local residents promotes the increase in activity space on weekends, while a high density of road and metro impedes the activity space on weekdays. Additionally, with increased job density, the activity space becomes smaller significantly throughout the week. Also, both on weekdays and weekends, the closer to the central business district (CBD), the smaller the activity space. This study can offer meaningful guidance to policymakers and city planners aiming to make the bikeshare distribution more reasonable.
@article{Ma2019, author = {X., Ma and Y., Ji and Y., Jin and J., Wang and M., He}, doi = {10.3390/su10113949}, issn = {20711050}, issue = {11}, journal = {Sustainability}, title = {Modeling the factors influencing the activity spaces of bikeshare around metro stations: A spatial regression model}, volume = {10}, year = {2018}, }